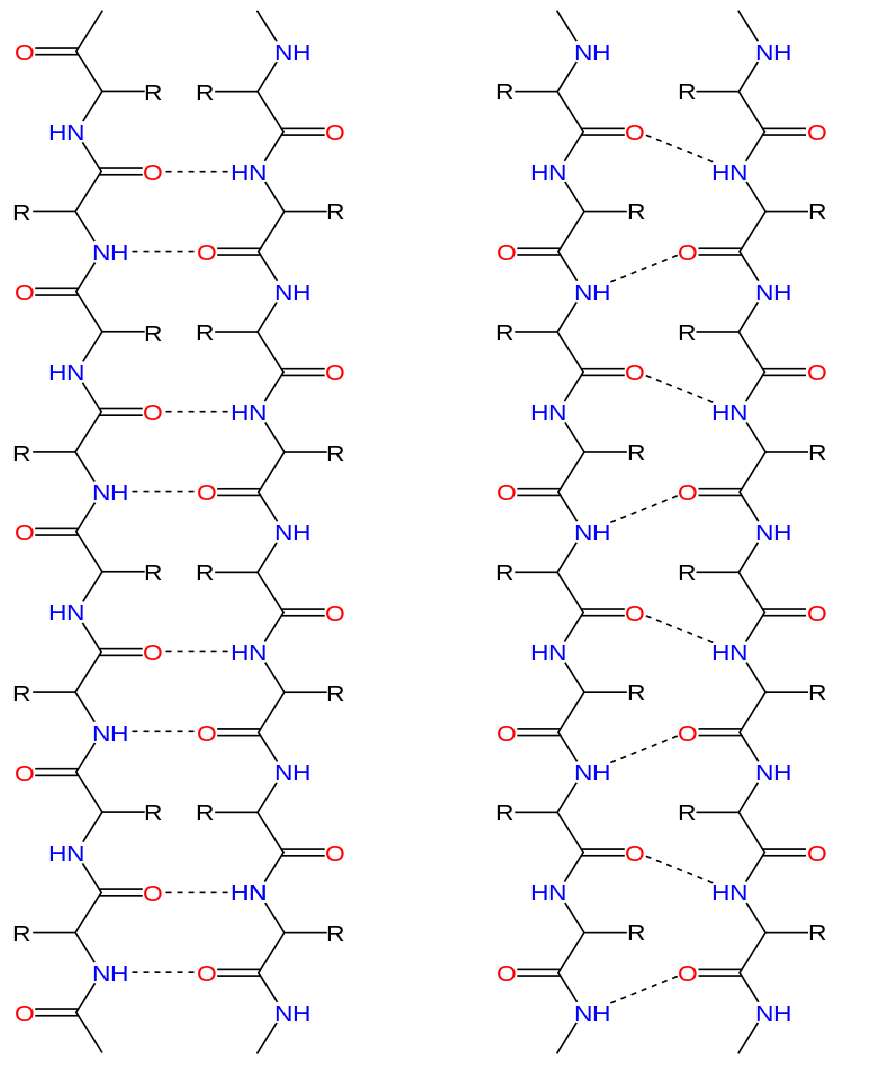
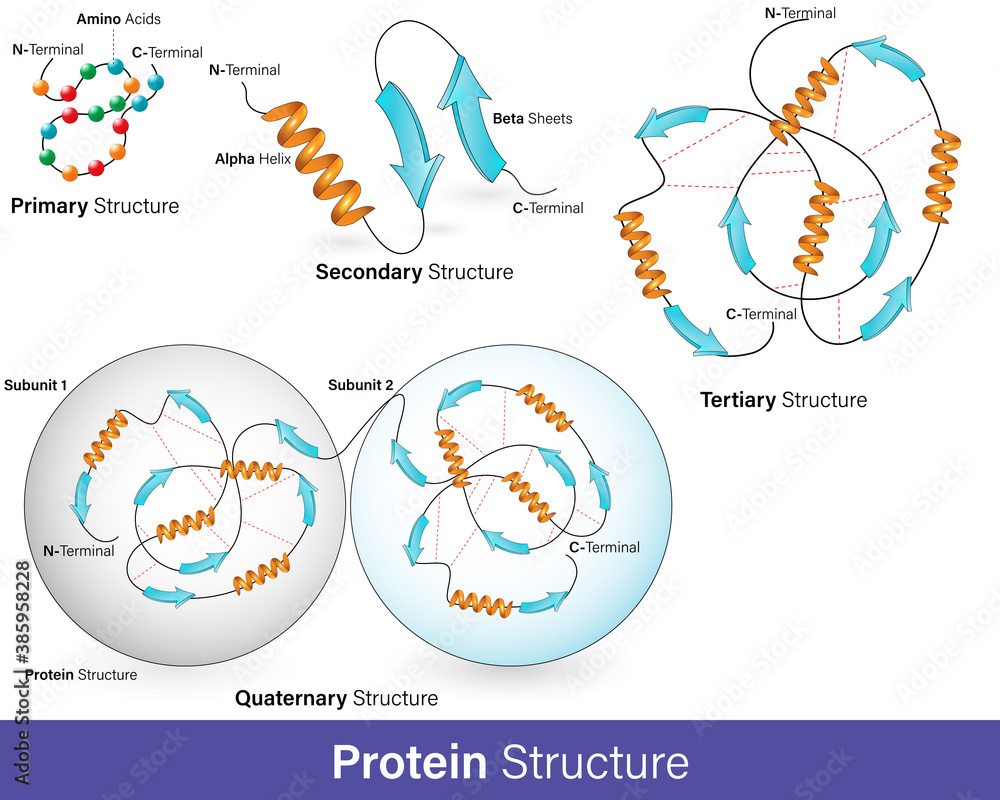
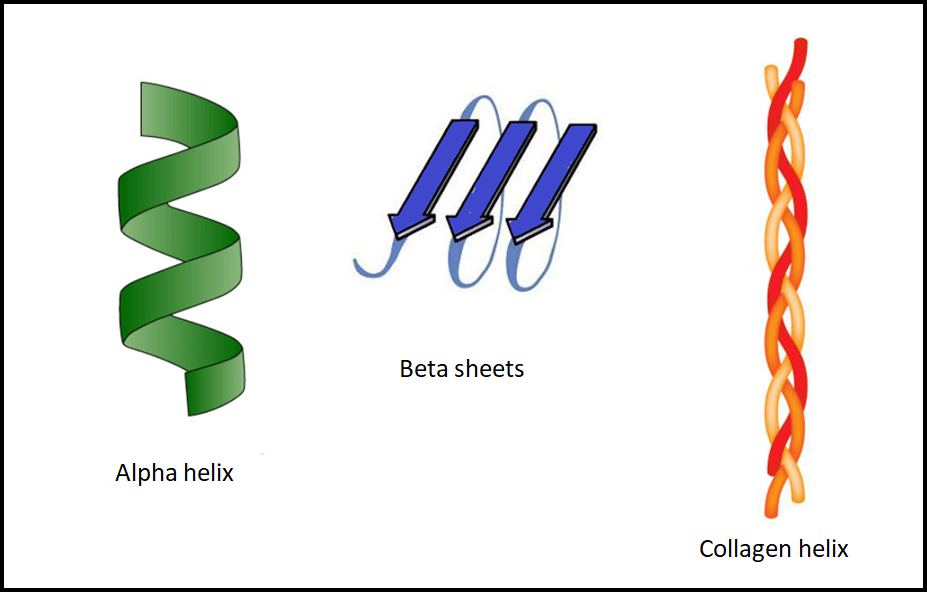
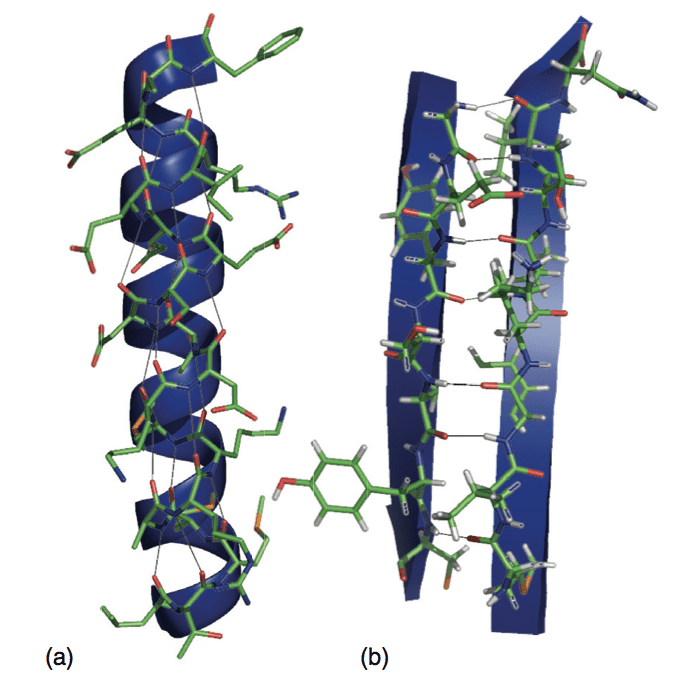What Are Alpha Helix And Beta Sheets - Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). The page provides a detailed exploration of secondary structures in proteins, focusing on alpha helices, beta sheets (parallel and. Alpha helices and beta sheets are both formed by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the.
The page provides a detailed exploration of secondary structures in proteins, focusing on alpha helices, beta sheets (parallel and. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). Alpha helices and beta sheets are both formed by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the.
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). Alpha helices and beta sheets are both formed by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h. The page provides a detailed exploration of secondary structures in proteins, focusing on alpha helices, beta sheets (parallel and.
Protein Structure Alpha Helix Beta Sheet 库存矢量图(免版税)1669950430
Alpha helices and beta sheets are both formed by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). The page provides a detailed exploration of secondary structures in proteins,.
Difference Between Alpha Helix and Beta Pleated Sheet
Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). Alpha helices and beta sheets are both formed by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the. The page provides a detailed exploration of secondary structures in proteins,.
vector illustration of Hierarchy of protein structure. alpha helix and
Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the. The page provides a detailed exploration of secondary structures in proteins, focusing on alpha helices, beta sheets (parallel and. Alpha helices and beta sheets are both formed by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o.
1. Secondary structure of protein, αhelix and βpleated sheet [118
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). Alpha helices and beta sheets are both formed by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h. The page provides a detailed exploration of secondary structures in proteins,.
Secondary structures of keratin protein (beta pleated sheets and alpha
Alpha helices and beta sheets are both formed by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h. The page provides a detailed exploration of secondary structures in proteins, focusing on alpha helices, beta sheets (parallel and. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the.
Difference between Alpha Helix and Beta Sheets YouTube
Alpha helices and beta sheets are both formed by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the. The page provides a detailed exploration of secondary structures in proteins,.
Alpha Helix Beta Sheet
Alpha helices and beta sheets are both formed by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). The page provides a detailed exploration of secondary structures in proteins,.
α helix & β sheet Protein secondary structure
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the. The page provides a detailed exploration of secondary structures in proteins, focusing on alpha helices, beta sheets (parallel and. Alpha helices and beta sheets are both formed by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the.
Difference Between Alpha Helical Form And Beta Sheet Like Protein at
The page provides a detailed exploration of secondary structures in proteins, focusing on alpha helices, beta sheets (parallel and. They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the. Alpha helices and beta sheets are both formed by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the.
onlymoli Blog
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the. The page provides a detailed exploration of secondary structures in proteins, focusing on alpha helices, beta sheets (parallel and. Alpha helices and beta sheets are both formed by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the.
The Page Provides A Detailed Exploration Of Secondary Structures In Proteins, Focusing On Alpha Helices, Beta Sheets (Parallel And.
They both are shaped by hydrogen bonding between the. Define the secondary structure of proteins and understand the structural features of major secondary structures, including \(\alpha\). Alpha helices and beta sheets are both formed by hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl o of one amino acid and the amino h.